
Decentralization is the defining feature of blockchain technology. Since a blockchain is a distributed public ledger, all transactions and assets can be easily viewed by everyone.
The decentralized nature of blockchain necessitates that the validity of each transaction is checked by several independent parties rather than a central authority. Each node in a network acts as a validator and must agree on whether or not a given transaction is valid. Nearly all blockchain networks have adopted this decentralized structure. However, the process of validating blocks or transactions can vary from one network to the next.
The differences between crypto minting and mining stem from the underlying methodologies (consensus mechanism) different blockchain networks use to validate blocks. In this blog, we examine the differences between crypto mining and minting and how they work.
What is cryptocurrency mining?
The term “mining” refers to the process via which the nodes (computers that perform the computations necessary to run a blockchain) of a blockchain network, also known as “miners,” validate blocks of transactions to ensure the continued security of the network in exchange for cryptocurrency incentives. Mining creates digital currency, and miners are compensated for keeping the network operational.
Mining, in a nutshell, is the process of validating transactions on the blockchain ledger using a combination of hardware processing power and software to solve a complicated algorithm and earn cryptocurrency as a reward for confirming transaction blocks.
To confirm and record each new transaction and guarantee the security of the blockchain, crypto mining requires specialized hardware to solve a hash, which is a hexadecimal string of 64 digits. Every participant engaged in the process is referred to as a network node.
These nodes compete to provide the most accurate solution for the hash of a transaction. The first node to acquire the solution is rewarded with freshly created cryptocurrency and is also responsible for updating the blockchain ledger with the new blocks.
Cryptocurrency mining completely depends on the huge computational resources of individual miners who participate voluntarily. Since thousands of transaction ledgers are saved locally on the miner’s computer, mining requires a lot of data and is not lucrative for individual miners.
Because of the occasional insufficiency of mining power, it is common practice for miners to pool their resources and create what is called a mining pool. A mining pool distributes its profits proportionally across its members.
To summarize, the steps involved in crypto mining are:
- First, the nodes validate the authenticity of the transactions.
- Next, individual transactions are appended to a list of other transactions to create a block.
- A hash and additional data are attached to the unconfirmed block.
- Miners then verify the block’s hash to guarantee its authenticity.
- Finally, after the block has been validated, it is recorded in the blockchain.
What is cryptocurrency minting?
When compared to crypto mining, crypto minting is a relatively new development. The term “minting” refers to the process by which new cryptocurrencies are created as incentives for validators (computers that verify transactions on a blockchain) to validate transaction blocks, authenticate data, and record new transaction blocks on the blockchain.
Cryptocurrency minting is based on the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism. Hence, it is closely related to staking. The staking mechanism is used by Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithms to synchronize the verification of transaction data and the validation of blocks.
Validators are like miners in a Proof-of-Work network. When comparing minting and mining a cryptocurrency, validators play a crucial part in establishing the differences between the two processes and their respective roles and requirements.
If a blockchain protocol is Proof-of-Stake, users can participate in the consensus process of the network as validators by “staking” the network’s native currency. The consensus method then uses a purely random and automated process to select the validators. Individuals that stake more cryptocurrencies in the network have a higher chance of being chosen as validators for confirming blockchain transactions.
Additional safeguards are built into the crypto minting system to ensure that validators are held liable for their mistakes. If a validator breaks the rules of the network, they risk losing all staked cryptocurrency. In the end, validators are compensated with a portion of the transaction fees that network users pay while using the Proof-of-Stake blockchain.
Cryptocurrency networks also mint other assets as tokens, such as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). However, it is essential to remember that coin minting and token minting are two very different processes.
NFTs are tokenized digital works of art, digital assets, certificates, digital collectibles, trading cards, etc. Unlike block validation, adding NFTs to the blockchain is not limited to only validators. Anybody with access to the internet can do it to store any kind of digital work or document on the distributed ledger. In the context of NFTs, minting refers to creating digital assets on the blockchain.
To summarize, the steps involved in crypto mining are:
- Validators deposit and risk a considerable amount of cryptocurrency to participate in Proof-of-Stake.
- Validators are chosen randomly to record and verify data on the blockchain.
- The larger the stakes, the better their chances of being chosen to record and validate the blockchain.
- Validators risk losing everything they have invested if they are found acting maliciously.
- Validators who run the validator node accept the costs and hazards of staking in exchange for the potential to profit from transaction fees paid by network users.
Is crypto mining and minting the same?
Coin minting and crypto mining are similar in that both seek to create new coins, but they go about it differently. Proof-of-Work is used in cryptocurrency mining, whereas Proof-of-Stake is used in cryptocurrency staking.
In the case of mining, blocks of transactions are verified by nodes executing mathematical computations. In the case of minting, validators stake the blockchain’s native cryptocurrency to verify batches of transactions.
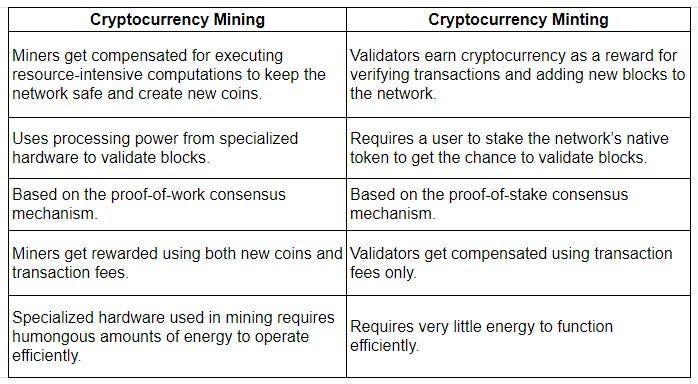
Difference between crypto mining and crypto minting
Minting and mining are two different processes for creating cryptocurrency, with minting focusing on the underlying consensus and mining focusing on creating new cryptocurrency as rewards. Minting cryptocurrencies involves a Proof-of-Stake consensus, whereas mining involves a Proof-of-Work consensus. While both methodologies are used to create new cryptocurrencies, they have different approaches to getting there.
Minting and mining ensure the decentralized distribution of freshly minted cryptocurrency via the blockchain. While minting is not technically part of mining, it does happen when a new block is hashed in the Bitcoin network.
Let’s summarize the significant differences between mining and minting:
Conclusion
The key difference between minting cryptocurrency and mining cryptocurrency is that one involves Proof-of-Work (PoW), while the other involves Proof-of-Stake (PoS). While both PoW and PoS minting lead to the same final result — new coins — the methods by which this transpires are different. Nonetheless, both systems aim to safeguard the blockchain and distribute new cryptocurrency in a decentralized manner.
Important Disclosures:
Certain statements in this document might be forward-looking statements, including those identified by the expressions “anticipate”, “believe”, “plan”, “estimate”, “expect”, “intend”, “target”, “seek”, “will” and similar expressions to the extent they relate to the material produced by Bytex staff member. Forward-looking statements are not historical facts but reflect the current expectations regarding future results or events. Such forward-looking statements reflect current beliefs and are based on information currently available to them. Forward-looking statements are made with assumptions and involve significant risks and uncertainties. Although the forward-looking statements contained in this document are based upon assumptions the author of the material believes to be reasonable, none of Bytex’s staff can assure potential participants and investors that actual results will be consistent with these forward-looking statements. As a result, readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these statements as a number of factors could cause actual results or events to differ materially from current expectations
The commentaries contained herein are provided as a general source of information based on information available as of MMMM DD, 2022. Every effort has been made to ensure accuracy in these commentaries at the time of publication; however, accuracy cannot be guaranteed. Market conditions may change investment decisions arising from the use or relevance of the information contained here. ByteX. makes no representation or warranty to any participant regarding the legality of any investment, the income or tax consequences, or the suitability of an investment for such investor. Prospective participants must not rely on this document as part of any assessment of any potential participation in buying and selling of virtual currency assets and should not treat the contents of this document as advice relating to legal, taxation, financial, or investment matters. Participants are strongly advised to make their own inquiries and consult their own professional advisers as to the legal, tax, accounting, and related matters concerning the acquisition, holding, or disposal of a virtual currency. All content is original and has been researched and produced by ByteX.

